12th Bio Botany2nd Assignment July 2021 Answer Key:- This is the 2nd assignment for 12th standard Bio Botany with answers. This is a full answer key for 12th standard Bio Botany both English and Tamil medium students

12th Bio Botany Tamil Medium 2nd Assignment July 2021(With Answers)
- Download 12th Bio Botany TM second assignment pdf only questions – Download Now
- Download 12th Bio Botany TM assignment pdf with answers only questions – Visit This Page
12th Bio Botany English Medium 2nd Assignment July 2021(With Answers)
- Download 12th Bio Botany EMsecond assignment pdf only questions – Download Now
- Download 12th Bio Botany EMassignment pdf with answers only questions – Visit This Page
Assignment
Class -12 Subject:Bio Botany
Unit 2
Chapter 2 – Classical Genetics
Part – A
I. One mark questions
1.The dominant epistatis ratio is
a) 9:3:3:1
b) 12:3:1
c) 9:3:4
d) 9:6:1
Answer :- b) 12:3:1
2.Fruit colour in squash is an example of
a) Recessive epistasis
b) Dominant epistasis
c) Complementary genes
d) Inhibitary genes
Answer :- b) Dominant epistasis
3.The term Genetics was introduced by……..
a) Gregor Johann Mendel
b) Erich Von Tscermak
c) W.Bateson
(d) Carl Correns
Answer :- c) W.Bateson
4.A gene can exist in alternate forms for the same trait is called ……..
a) Hybrids
b) Alleles
c) Hereditary units
d) Factors
Answer :- b) Alleles
5.Observable characteristic of an organism is.
a) Genotype
b) Phenotype
c) Hybrid
d) Variation
Answer :- b) Phenotype
6.The result of Mendel’s dihybrid cross led him to propose____
a) Law of dominance
b) Law of segregation
c) Law of independent assortment
d) Law of hybrid
Answer :- c) Law of independent assortment
7.It is a genetic cross which involves individuals diffusing in two charcters.
a)Monohybrid cross
b) Trihybridcross
c) Dihybridcross
d) Test cross
Answer :- c) Dihybridcross
8.Introgenic interaction does not includes……….
a) Complete dominance
b) Codominance
c) Incomplete dominance
d) Multiple alleles
Answer :- d) Multiple alleles
9.An allele which has the potential to cause the death of an organism is called…….
a) Multiple alleles
b) Lethal allele
c) Single allele
d) Dominant allele
Answer :- b) Lethal allele
10.Dominant epistasis is found in…….
a) Antirrhinum
b) Squash fruit
c) Garden pea
d) Wheat
Answer :- b) Squash fruit
Part – B
II.Very Short Answer.
1.Define Genetics?
It is the branch of biological science which deals with the mechanism of transmission of characters from parent to off-springs.
2.What is Population Genetics?
Population Genetics – Deals with heredity in groups of individuals for traits which is determined by a few genes.
3.What is Codominance?
This pattern occurs due to simultaneous (joint) expression of both alleles in the heterozygote – The phenomenon in which two alleles are both expressed in the heterozygous individual is known as codominance. Example. Red and white flowers of Camellia, inheritance of sickle cell hemoglobin. ABO blood group system in humanbeings
4.What are the 4 types of gametes formed by the influence of dihybridcross
1.Yellow round (YR) -9/16
2.Yellow Wrikled (Yr) – 3/16
3.Green round (yR) – 3/16
4. Green wrinkled (yr) -1/16
5.What is Dihybrid cross?
It is a genetic cross that involves individuals differing in two characters. Dihybrid inheritance is the inheritance of two separate genes each with two alleles.
Part – C
III. Short Answer.
1.What is incomplete dominance.
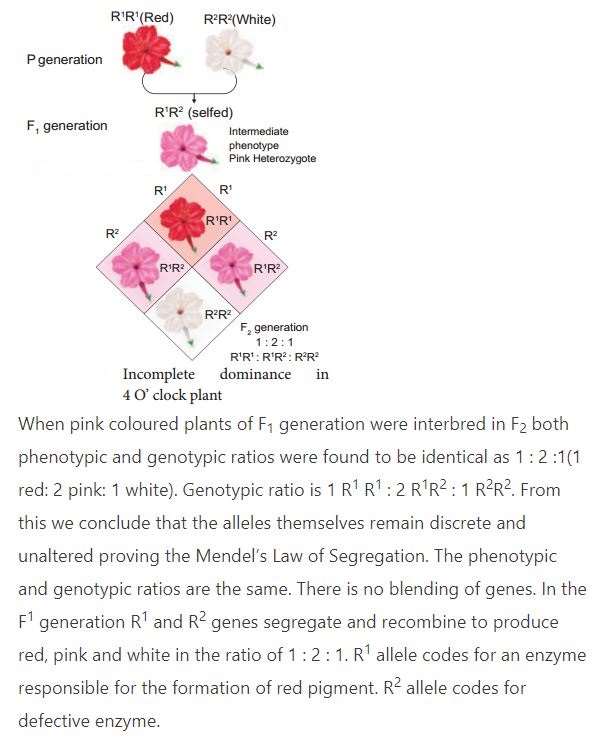
The German Botanist Carl Correns’s (1905) Experiment – In 4 O’ clock plant, Mirabilis jalapa when the pure breeding homozygous red (R1R1) parent is crossed with homozygous white (R2R2), the phenotype of the F1 hybrid is heterozygous pink (R1R2). The F1 heterozygous phenotype differs from both the parental homozygous phenotype. This cross did not exhibit the character of the dominant parent but an intermediate colour pink. When one allele is not completely dominant to another allele it shows incomplete dominance. Such allelic interaction is known as incomplete dominance. F1 generation produces intermediate phenotype pink coloured flower.
2.What is epistatic.
It is a gene interaction in which two alleles of a gene at one locus interfere and suppress or mask the phenotypic expression of a different pair of alleles of another gene at another locus. The gene that suppresses or masks the phenotypic expression of a gene at another locus is known as epistatic
3.What is Reciprocal cross.
Reciprocal cross – In one experiment, the tall pea plant were pollinated with the pollens from true-breeding plants, the result was all tall plants, when the parental types were reversed, the pollen from a tall plant was used to pollinate a dwarf pea plant which gave only tall plants. The result was the same – All tall plant(♀) x Dwarf (♂) and Tall (♂) x Dwarf ( ♀ ) matting are done in both ways which are called reciprocal crosses. The results of the reciprocal crosses are the same. So it was concluded that the trait is not sex dependent
4.Define Genetics.
“Genetics” is the branch of biological science which deals with the mechanism of transmission of characters from parents to off springs. The term Genetics was introduced by W. Bateson in 1906
The four major subdisciplines of genetics are
(a) Classical genetics
(b) Molecular genetics
(c) Population genetics
(d) Quantitative genetics
5.Define Atavism.
Atavism is a modification of a biological structure whereby an ancestral trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary changes in the previous generations. Evolutionary traits that have disappeared phenotypically do not necessarily disappear from an organism’s DNA. The gene sequence often remains, but is inactive.
Such an unused gene may remain in the genome for many generations. As long as the gene remains intact, a fault in the genetic control suppressing the gene can lead to the reappearance of that character again. Reemergence of sexual reproduction in the flowering plant Hieracium pilosella is the best example for Atavism in plants
Part – D
IV.Write in detail.
1 .Write the importance of variations.
- They help the individuals to adapt themselves to the changing environment.
- Variations allow breeders to improve better yield, quicker growth, increased resistance and lesser input.
- They constitute the raw materials for evolution.
2.Explain incomplete dominance in Mirabilis jalapa.


1 COMMENTS
Comments are closed.