12th Chemistry 2nd Assignment for July 2021 (with Answers) :- This is the full answerkey for 12th Chemistry 2nd Assignment for July 2021 Tamilnadu Stateboard Students.Please download using the following links

12th Chemistry English Medium 2nd Assignment July 2021 Answerkey
- Download 12th Chemistry English Medium second assignment pdf only questions – Download Now
- Download 12th Chemistry English Medium assignment pdf with answers only questions – Visit This Page
12th Botany Tamil Medium 2nd Assignment July 2021 Answerkey
- Download 12th Chemistry Tamil Medium second assignment pdf only questions – Download Now
- Download 12th Chemistry Tamil Medium assignment pdf with answers only questions – Visit This Page
Assignment
Class – 12 Subject:Chemistry (Unit 2and 3)
Unit 2- P Block elements –I
Part – A
I. Choose the correct answer.
1.An aqueous solution of borax is
a) Neutral
b) Acidic
c) Basic
d) Amphoteric
Answer:- c) Basic
2.Which of the following metals has the largest abundance in the earth’s crust?
a) Aluminium
b) Calcium
c) Magnesium
d) Sodium
Answer:- a) Aluminium
3.In diborane, the number of electrons that accounts for banana bonds is
a) Six
b) Two
c) Four
d) Three
Answer:- c) Four
4.The element that does not show catenation among the following p-block elements is
a) Carbon
b) Silicon
c) Lead
d) Germanium
Answer:- c) Lead
5.Carbon atoms in fullerene with formula C60 have
a) sp3 hybridised
b) sp hybridised
c) sp2 hybridised
d) partially sp2 and partially sp3 hybridised
Answer:- c) sp2 hybridised
6.Oxidation state of carbon in its hydrides
a) 4
b) – 4
c) + 3
d) + 2
Answer:- a) +4
7.Which of the following is not sp2 hybridised
a) Graphite
b) Grapheme
c) Fullerene
d)Dry ice
Answer:- d)Dry ice
8.The geometry at which carbon atom in diamond are bonded to each other is
a) Tetrahedral
b) Hexagonal
c) Octahedral
d) None of these
Answer:- a) Tetrahedral
9.Thermodynamically the most stable form of carbon is
a) Diamond
b) Graphite
c) Fullerene
d) None of these
Answer:- b) Graphite
10 .The compounds that is used in nuclear reactors as protective shields and control rods is
a) Metal borides
b) Metal oxides
c) Metal carbonates
d) Metal carbide
Answer:- a) Metal borides
Part – B
II.Very Short Answer.
1.What is catenation ? Describe briefly the catenation property of carbon.
Catenation:
It is the phenomenon of an atom to form a strong covalent bond with the atoms of itself. Carbon shares the property of catenation to maximum extent because it is small in size and can form pn-pn multiple bonds to itself. The following conditions are necessary for catenation.
- The valency of element is greater than or equal to two.
- Element should have an ability to bond with itself.
- The self bond must be as strong as its bond with other elements.
- Kinetic inertness of catenated compound towards other molecules. Carbon possesses all the above properties and forms a wide range of compounds with itself.
2.Give the uses of silicones.
- Silicones are used for low temperature lubrication and in vacuum pumps, high temperature oil baths etc.
- They are used for making water proofing clothes.
- They are used as insulting material in electrical motor and other appliances
- They are mixed with paints and enamels to make them resistant towards high temperature, sunlight, dampness and chemicals.
3. AlCl3 behaves like a lewis acid. Substantiate this statement.
In AlCl3, Al an electron-deficient it needs two electrons to complete octet so it acts as lewis acid. AlCl3 usually exists as a dimer to achieve octet by bridged Cl atom electron-deficient compounds are lewis acids.
4.Write a note on metallic nature of p-block elements.
- The tendency of an element to form a cation by loosing electrons is known as electro¬positive or metallic character.
- This character depends on the ionisation energy.
- Generally on descending a group the ionisation energy decreases and hence the metallic character increases.
In p-block, the elements present in lower left part are metals while the elements in the upper right part are non metals. Elements of group 13 have metallic character except the first element boron which is a metalloid, having properties intermediate between the metal and nonmetals. The atomic radius of boron is very small and it has relatively high nuclear charge and these properties are responsible for its nonmetallic character.
In the subsequent groups the non-metallic character increases. In group 14 elements, carbon is a nonmetal while silicon and germanium are metalloids. In group 15, nitrogen and phosphorus are non metals and arsenic & antimony are metalloids. In group 16, oxygen, sulphur and selenium are non metals and tellurium is a metalloid. All the elements of group 17 and 18 are non metals.
5.CO is a reducing agent . Justify with an example.
Both thermodynamic and kinetic factors make carbon monoxide (CO) a better reducing agent. When CO is used to reduce a metal oxide, it gets oxidized to CO2 Thermodynamically, CO2 is much more stable than CO. For example,
CO + Fe2O3 → 2Fe + 3CO2
Part – C
III. Short Answer.
1.How will you identify borate radical?
When boric acid or borate salt is heated with ethyl alcohol in presence of concentrated H2SO4, an ester triethyl borate is formed. The Vapour of this ester burns with a green edged flame and this reaction is used to identify the presence of borate.
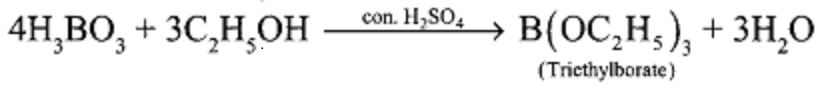
2.Give the uses of Borax.
- Borax is used for the identification of coloured metal ions.
- In the manufacture optical and borosilicate glass, enamels and glazes for pottery.
- It is also used as a flux in metallurgy and also acts as a good preservative.
3.Give the structure of CO and CO2.
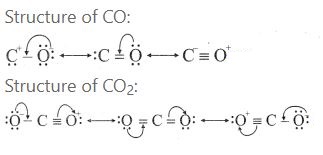
4.Write a note on Fisher Tropsch Synthesis.
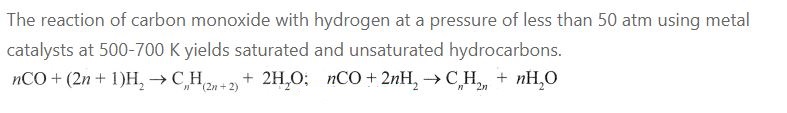
5.Write a short note on anamolous properties of the first element of p-block.
In p-block elements the first member of each group differs from the other elements of the corresponding group. The following factors are responsible for this anomalous behavior.
- Small size of the first member.
- High ionisation enthalpy and high electronegativity.
- Absence of d-orbitals in their valance shell.
The first member of group-13, boron is a metalloid while others are reactive metals. Moreover, boron shows a diagonal relationship with silicon of group -14. The oxides of boron and silicon are similar in their acidic nature.
Part – D
IV.Write in detail.
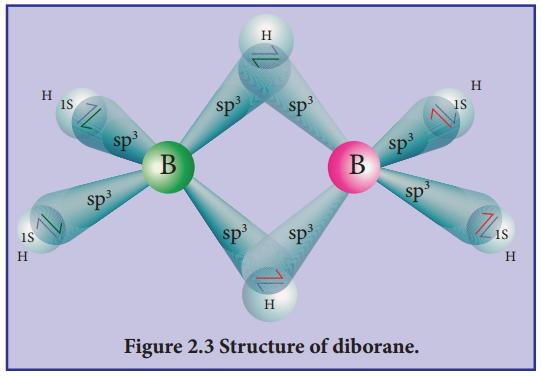
1.Describe the structure of diborane.
In diborane two BH2 units are linked by two bridged hydrogens. Therefore, it has eight B-H bonds. However, diborane has only 12 valance electrons and are not sufficient to form normal covalent bonds. The four terminal B-H bonds are normal covalent bonds (two centre – two electron bond or 2c-2e bond). The remaining four electrons have to used for the bridged bonds, i.e. two three centred B-H-B bonds utilise two electrons each.
Hence, these bonds are three centre – two electron bonds. The bridging hydrogen atoms are in a plane as shown in the figure. In dibome, the boron is sp3 hybridised. Three of the four sp3 hybridised orbitals contains single electron and the fourth orbital is empty.
Two of the half filled hybridised orbitals of each boron overlap with the two hydrogens to form four terminal 2c-2e bonds, leaving one empty and one half filled hybridised orbitals on each boron. The Three centre – two electron bonds, B-H-B bond formation involves overlapping the half filled hybridised orbital of one boron, the empty hybridised orbital of the other boron and the half filled 1s orbital of hydrogen
2.Write a note on zeolites.
- Zeolites are three dimensional crystalline solids containing aluminium, silicon and oxygen in their regular three dimensional framework.
- They are hydrated sodium alumino silicates with general formula, Na2O. (Al2O3). x(SiO2)y(H2O) (x = 2 to 10; y = 2 to 6)
- Zeolites have porous structure in which the monovalent sodium ions and water molecules are loosely held.
- The Si and Al atoms are tetrahederally coordinated with each other through shared oxygen atoms.
- Zeolites structure looks like a honeycomb consisting of a network of interconnected tunnels and cages.
- Zeolite crystal to act as a molecular sieve. They helps to remove permanent hardness of water.
Unit 3- P Block elements –II
Part – A
I. Choose the correct answer.
1.An element belongs to group 15 and 3 rd period of the periodic table, its
electronic configuration would be
a) 1s2 2s2 2p4
b) 1s2 2s2 2p3
c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
Answer:- d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
2.P4O6 reacts with cold water to give
a) H3PO3
b) H4P2O7
c) HPO3
d) H3PO4
Answer:- a) H3PO3
3.The basicity of ortho phosphorus acid ( H4PO3) is
a) 3
b) 2
c) 1
d) 4
Answer:- b) 2
4.Amon the ollo in hich is he trongest o idizing agen ?
a) Cl2
b) F2
c) Br2
d) I2
Answer:- b) F2
5.Most easily liquefiable gas is
a) Ar
b) Ne
c) He
d) Kr
Answer:- c) He
6.Which is the strongest acid among the hydrogen halide
a) HI
b) HF
c) HBr
d) HCl
Answer:- a) HI
7.When copper is heated with Conc HNO3 it produces
a) Cu(NO3)2 , NO and NO2
b) Cu(NO3)2 and N2O
c) Cu(NO3)2 and NO2
d) Cu(NO3)2 and NO
Answer:- c) Cu(NO3)2 and NO2
8.The oxidation state of oxygen in OF2 is………
a) +2
b) -2
c) +1
d) 0
Answer:- d) 0
9.The radioactive inert gas is ……….
a) He
b) Ne
c) Ar
d) Rn
Answer:- d) Rn
10.An example for interhalogen compound is……
a) ICl
b) BrF3
c) IF7
d) All the above
Answer:- d) All the above
Part – B
II.Very Short Answer.
1.What is inert pair effect?
In p-block elements, as we go down the group, two electrons present in the valence s-orbital become inert and are not available for bonding (only p-orbital involves chemical bonding). This is called inert pair effect.
2.What are inter halogen compounds? Give examples.
Each halogen combines with other halogens to form a series of compounds called interhalogen compounds. For example, Fluorine reacts readily with oxygen and forms difluorine oxide (F2O) and difluorine dioxide (F2O2).
3.Mention any two uses of chlorine.
- Purification of drinking water
- Bleaching of cotton textiles, paper and rayon
- It is used in extraction of gold and platinum
4.Give a test for sulphate ion.
5.Write down the hybridisation and shape for the compounds of Xenon
a) XeF4 b) XeO3
Part – C
III. Short Answer.
1.Give the reason to support the sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is a dehydrating
agent.

2.Give the uses of helium.
- Helium and oxygen mixture is used by divers in place of air oxygen mixture. This prevents the painful dangerous condition called bends.
- Helium is used to provide inert atmosphere in electric arc welding of metals
- Helium has lowest boiling point hence used in cryogenics (low temperature science).
- It is much less denser than air and hence used for filling air balloons
3.Write the structural formula and molecular formula for the following
compounds.
a) Nitric acid b) Phosphoric acid
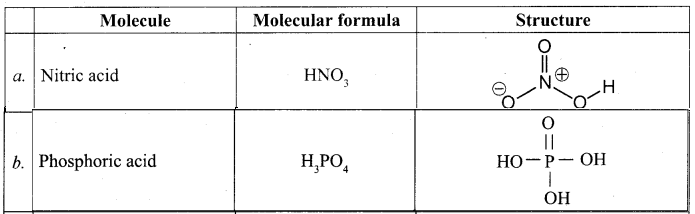
4.Why HF is a weak acid, where as the binary acids of all others
halogens are strong acids ?
The hydrogen halides are extremely soluble in water due to the ionisation.
X + H2O → H3O+ + X–
( X = F, Cl, Br or I )
Solutions of hydrogen halides are therefore acidic and known as hydrohalic acids. Hydrochloric, hydrobromic and hydroiodic acids are almost completely ionised and are therefore strong acids but HF is a weak acid. For HF,
- HF + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + F–
- HF + F– → HF–2
At high concentration, the equilibrium involves the removal of fluoride ions is important. Since it affects the dissociation of hydrogen fluoride, therefore it is a weak acid.
5.Write the reason for the anamolous behaviour of nitrogen.
1. Due to its small size, high electro negativity, high ionisation enthalpy and absence of d-orbitals.
2. N, has a unique ability to form pπ – pπ multiple bond whereas the heavier members of this group (15) do not form pπ – pπ bond, because their atomic orbitals are so large and diffused that they cannot have effective overlapping.
3. Nitrogen exists a diatomic molecule with triple bond between the two atoms whereas other elements form single bond in the elemental state.
4. N cannot form dπ – pπ bond due to the absence of d – orbitals whereas other elements can.
Part – D
IV.Write in detail.
1.Explain Deacons process.

2.Complete the following reactions.
i. Na2SiO3 + 6HF →
Na2SiO3 + 6HF → Na2SiF6 + 3H20
ii. XeO2F2 + SiO2 →
XeO2F2 + SiO2 → 2XeO3 + SiF4
iii. XeO2F2 + SiO2 →
XeO2F2 + SiO2 → 3NaH2P02 + PH3↑
iv. NaCl + MnO2 + H2SO4 →
NaCl + MnO2 + H2SO4 → cl2 + Mncl2+ 4NaHSO4 +2H2O
v. KClO3 →
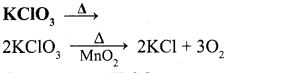
4 COMMENTS
Comments are closed.


Please give all subjects assignment of 12
There is no Answer for 4th And 5th In Very Short Answer.
It’s so helpful too all